The Gig Economy: Challenges and Opportunities for UPSC 2025
Related Articles: The Gig Economy: Challenges and Opportunities for UPSC 2025
- The Hyundai IONIQ 5: Unveiling The Electrifying Future In 2025
- How Many Days Until January 1, 2025?
- The Land Before Time: Journey Of The Brave (2016)
- How Long Until March 2, 2025: A Comprehensive Countdown
- Form 202-I IRS: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Gig Economy: Challenges and Opportunities for UPSC 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Video about The Gig Economy: Challenges and Opportunities for UPSC 2025
The Gig Economy: Challenges and Opportunities for UPSC 2025

Introduction
The gig economy, characterized by the prevalence of short-term, flexible work arrangements, has emerged as a significant force in the global labor market. With the advent of digital platforms and technological advancements, more and more individuals are opting for freelance work, contract-based employment, and other non-traditional forms of work. This trend poses both challenges and opportunities for the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC), the body responsible for recruiting civil servants in India.
Challenges
1. Job Security and Benefits:
Gig workers typically lack the job security and benefits enjoyed by traditional employees. They may face income volatility, limited access to health insurance, and fewer opportunities for professional development. This can make it difficult for gig workers to plan for the future and may discourage talented individuals from pursuing careers in the public sector.
2. Regulation and Labor Rights:
The gig economy often operates in a regulatory gray area, with gig workers falling outside the purview of traditional labor laws. This can lead to exploitation, wage theft, and a lack of protection for gig workers’ rights. The UPSC must address these issues to ensure that gig workers are treated fairly and that the public sector remains an attractive option for skilled individuals.
3. Skills Gap:
The gig economy requires workers to possess a diverse range of skills, including digital literacy, adaptability, and problem-solving abilities. However, many gig workers may lack these skills, which can limit their opportunities and hinder their ability to contribute effectively to the public sector. The UPSC must invest in training and upskilling programs to bridge this skills gap.
Opportunities
1. Flexibility and Diversity:
The gig economy offers flexibility and diversity in work arrangements, allowing individuals to balance work and personal commitments. This can be particularly appealing to women, individuals with disabilities, and those seeking to return to the workforce after a career break. The UPSC can leverage this flexibility to attract a wider pool of candidates from diverse backgrounds.
2. Innovation and Entrepreneurship:
The gig economy fosters innovation and entrepreneurship by providing a platform for individuals to develop new products and services. Gig workers can bring fresh ideas and perspectives to the public sector, helping to drive innovation and improve service delivery. The UPSC should encourage gig workers to participate in public service and provide opportunities for them to contribute their expertise.
3. Cost-Effectiveness:
Hiring gig workers on a project-based basis can be more cost-effective than traditional employment arrangements. The UPSC can utilize the gig economy to fill temporary staffing needs, reduce overhead costs, and optimize resource allocation.
Recommendations for UPSC 2025
To address the challenges and capitalize on the opportunities presented by the gig economy, the UPSC should consider the following recommendations:
1. Regulatory Framework:
Develop a comprehensive regulatory framework that defines the rights and responsibilities of gig workers and ensures their fair treatment. This framework should address issues such as minimum wage, working conditions, and access to benefits.
2. Skills Development:
Invest in training and upskilling programs to equip gig workers with the skills necessary to succeed in the public sector. These programs should focus on developing digital literacy, analytical abilities, and problem-solving skills.
3. Flexible Hiring Practices:
Adopt flexible hiring practices that allow the UPSC to engage gig workers on a project-based or contract basis. This will enable the UPSC to access a wider pool of candidates and fill temporary staffing needs efficiently.
4. Gig Worker Representation:
Establish a platform or mechanism for gig workers to voice their concerns and provide input on policies that affect them. This will ensure that the UPSC takes the perspectives of gig workers into account when making decisions.
5. Collaboration with Industry:
Collaborate with industry partners to develop innovative ways to engage gig workers in public service. This could include creating mentorship programs, offering internships, or establishing partnerships with digital platforms.
Conclusion
The gig economy presents both challenges and opportunities for the UPSC. By addressing the challenges related to job security, regulation, and skills gaps, and by leveraging the opportunities for flexibility, innovation, and cost-effectiveness, the UPSC can harness the potential of the gig economy to improve public service delivery and attract a diverse and talented workforce. As the UPSC prepares for UPSC 2025, it is imperative to consider these recommendations and adapt to the changing landscape of the labor market to ensure the continued success and relevance of the civil service in India.



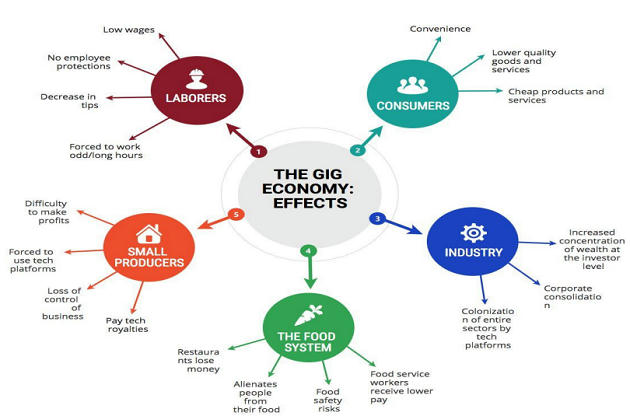
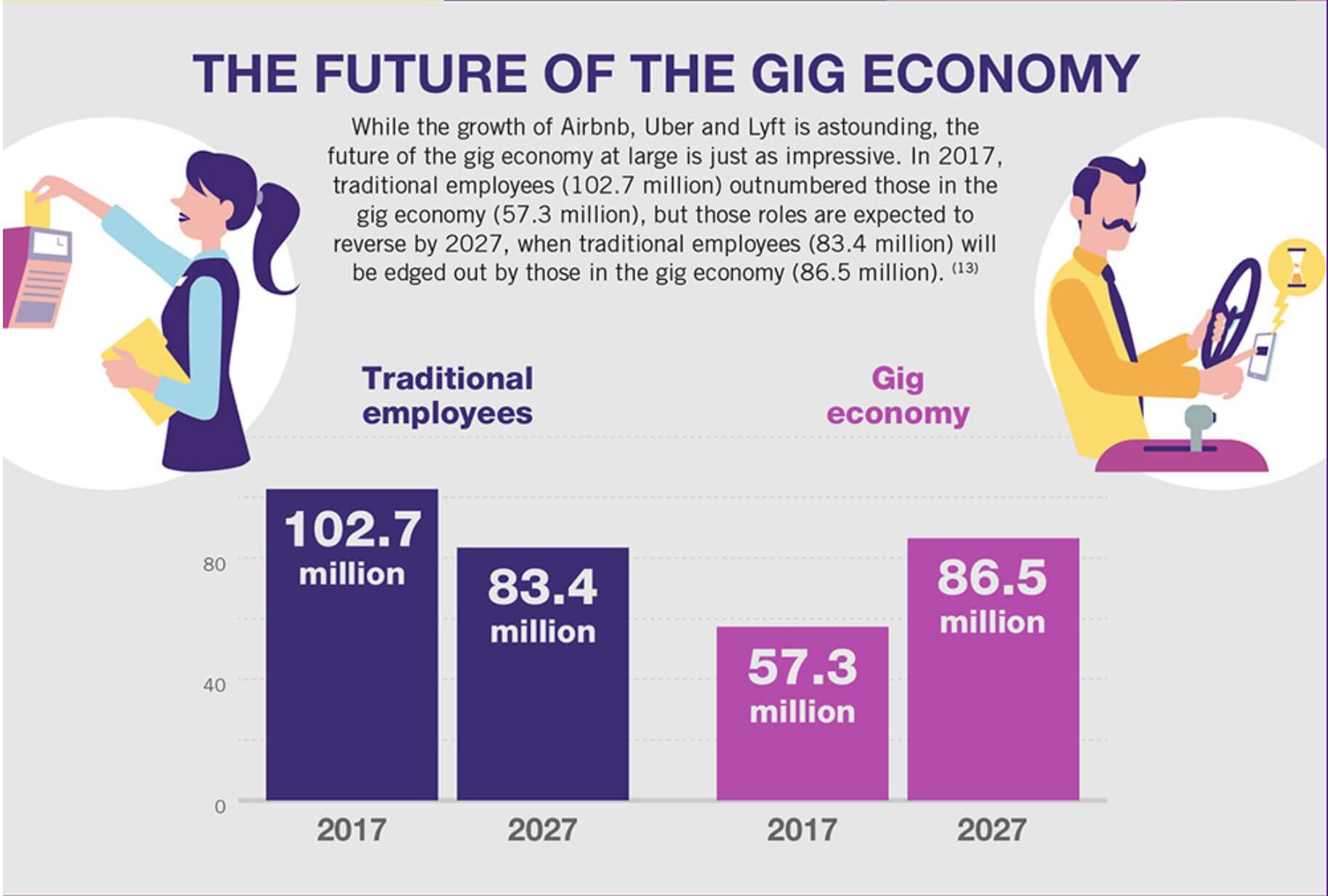

![The History and Future of the Gig Economy [Infographic] - Business2Community](https://www.business2community.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/gigworker-the-history-and-future-of-the-gig-economy-snip.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Gig Economy: Challenges and Opportunities for UPSC 2025. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
