Plan Nacional del Buen Vivir 2013-2025: A Holistic Approach to Sustainable Development in Ecuador
Related Articles: Plan Nacional del Buen Vivir 2013-2025: A Holistic Approach to Sustainable Development in Ecuador
- Timeshare Calendar 2025: A Comprehensive Guide To Planning Your Vacations
- Volvo XC40 Recharge 2025: A Comprehensive Review
- Can I Replace A 2025 Battery With A 2032?
- Project 2025: Transforming The Future Of Sustainability
- 2025 Land Cruiser Prado: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Plan Nacional del Buen Vivir 2013-2025: A Holistic Approach to Sustainable Development in Ecuador. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Video about Plan Nacional del Buen Vivir 2013-2025: A Holistic Approach to Sustainable Development in Ecuador
Plan Nacional del Buen Vivir 2013-2025: A Holistic Approach to Sustainable Development in Ecuador

Introduction
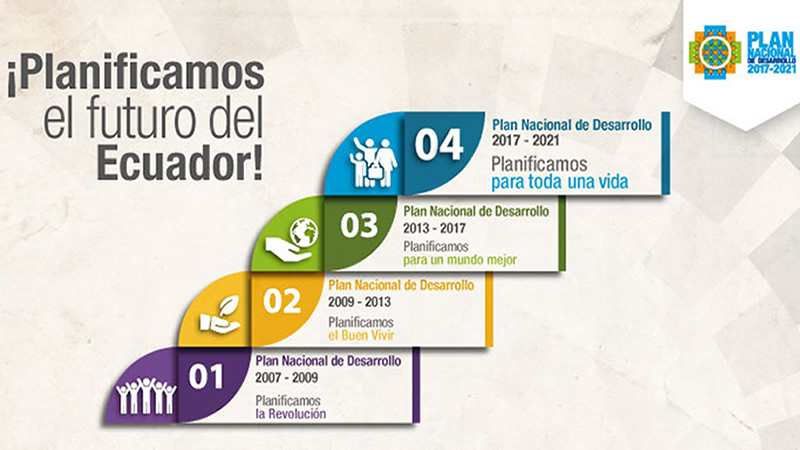
In 2013, Ecuador embarked on an ambitious journey towards sustainable development with the adoption of the Plan Nacional del Buen Vivir (PNBV) 2013-2025. The PNBV is a comprehensive roadmap that aims to create a society that values human well-being, environmental sustainability, and social justice. This article examines the key principles, objectives, and achievements of the PNBV, highlighting its innovative approach to development.
Principles and Objectives
The PNBV is founded on the concept of "buen vivir," which translates to "good living." This philosophy emphasizes the importance of a balanced and harmonious life that encompasses physical, mental, emotional, and spiritual well-being. The PNBV’s objectives are to:
- Eradicate poverty and reduce inequality
- Guarantee the rights of all citizens
- Promote sustainable economic growth
- Protect the environment
- Strengthen democracy and citizen participation
Key Pillars
The PNBV is structured around 12 key pillars, each addressing a different aspect of sustainable development. These pillars include:
- Education: Promoting quality education for all
- Health: Ensuring access to comprehensive healthcare
- Housing: Providing affordable and decent housing
- Employment: Creating decent and productive jobs
- Food sovereignty: Guaranteeing access to nutritious food
- Environmental sustainability: Protecting natural resources and mitigating climate change
- Cultural diversity: Preserving and promoting Ecuador’s rich cultural heritage
- Citizen security: Ensuring a safe and secure environment for all
- Social inclusion: Empowering marginalized groups
- Participatory democracy: Strengthening citizen involvement in decision-making
- Human mobility: Promoting safe and orderly migration
- Science, technology, and innovation: Fostering knowledge and innovation for development
Achievements and Impact
Since its implementation, the PNBV has made significant progress towards its objectives. Key achievements include:
- Reduced poverty and inequality: Ecuador’s poverty rate has decreased from 37% in 2013 to 25% in 2021.
- Improved education: The literacy rate has increased from 91% to 96%, and access to higher education has expanded.
- Enhanced healthcare: Universal healthcare coverage has been achieved, and maternal mortality rates have declined.
- Protected the environment: Ecuador has established the Yasuní National Park, one of the most biodiverse areas in the world.
- Strengthened democracy: Citizen participation in decision-making has increased through mechanisms such as participatory budgeting.
Innovative Features
The PNBV is notable for its innovative features, which set it apart from traditional development plans:
- Focus on well-being: The PNBV places human well-being at the center of development, rather than solely focusing on economic growth.
- Holistic approach: It integrates social, economic, environmental, and cultural dimensions of development into a single framework.
- Participatory design: The PNBV was developed through extensive consultations with citizens, ensuring that their needs and priorities were reflected in the plan.
- Monitoring and evaluation: A robust monitoring and evaluation system tracks progress towards the PNBV’s objectives and allows for adjustments as needed.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite its achievements, the PNBV has also faced challenges. Economic fluctuations, political instability, and the COVID-19 pandemic have impacted its implementation.
Looking ahead, the PNBV 2025-2030 is currently under development, building on the successes and addressing the challenges of the previous plan. The new plan will continue to prioritize human well-being, environmental sustainability, and social justice, while adapting to emerging challenges such as climate change and technological advancements.
Conclusion
The Plan Nacional del Buen Vivir 2013-2025 is a visionary and transformative development plan that has made significant progress towards creating a more just, equitable, and sustainable society in Ecuador. Its innovative approach to development, with a focus on well-being and participatory decision-making, serves as a model for other countries seeking to achieve sustainable development. As Ecuador embarks on the next phase of its PNBV journey, it remains committed to building a future where all citizens can live a life of dignity and fulfillment.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Plan Nacional del Buen Vivir 2013-2025: A Holistic Approach to Sustainable Development in Ecuador. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!