Hydrogen Fuel Cells: A Clean and Efficient Energy Source for the Future
Related Articles: Hydrogen Fuel Cells: A Clean and Efficient Energy Source for the Future
- FSA Rollover 2025 To 2026: Maximizing Your Tax-Advantaged Savings
- Bedford Street, Johnstown, PA: A Historical And Cultural Tapestry
- The 2025 Toyota 4Runner: A Comprehensive Review Of The Sixth-Generation Off-Road Icon
- 2025 Toyota RAV4: A Comprehensive Overview
- Carnival Mardi Gras Cruises 2025: An Unforgettable Voyage To The Heart Of Carnival’s Fun
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Hydrogen Fuel Cells: A Clean and Efficient Energy Source for the Future. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Video about Hydrogen Fuel Cells: A Clean and Efficient Energy Source for the Future
Hydrogen Fuel Cells: A Clean and Efficient Energy Source for the Future
Introduction
In the face of growing environmental concerns and the depletion of fossil fuels, the search for sustainable and environmentally friendly energy sources has become paramount. Among the various alternatives that have emerged, hydrogen fuel cells have garnered significant attention due to their potential to revolutionize the transportation and energy sectors. This article delves into the intricacies of hydrogen fuel cells, exploring their mechanisms, advantages, and potential applications, while also examining the challenges and future prospects of this promising technology.
Understanding Hydrogen Fuel Cells
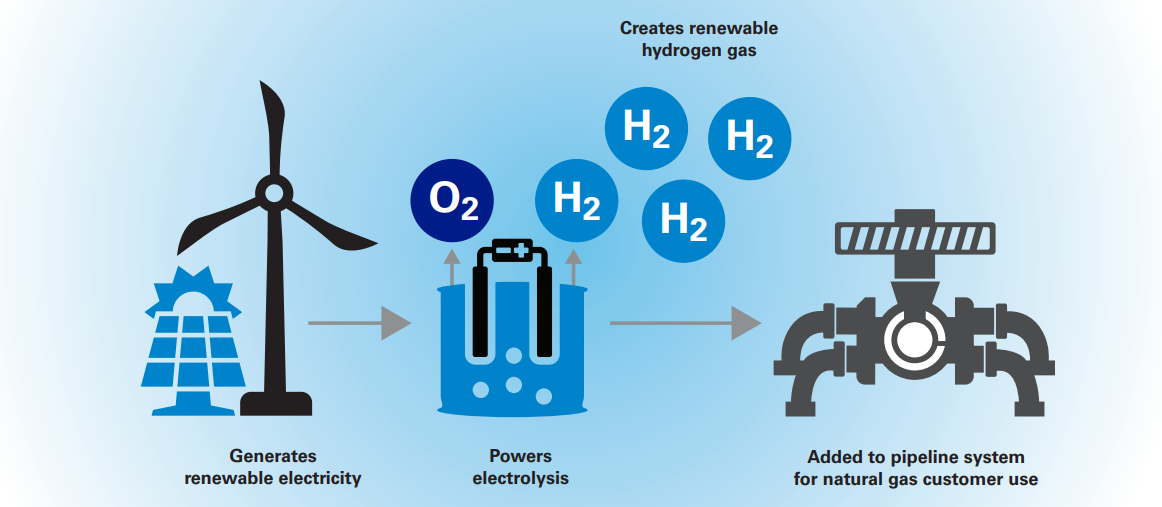
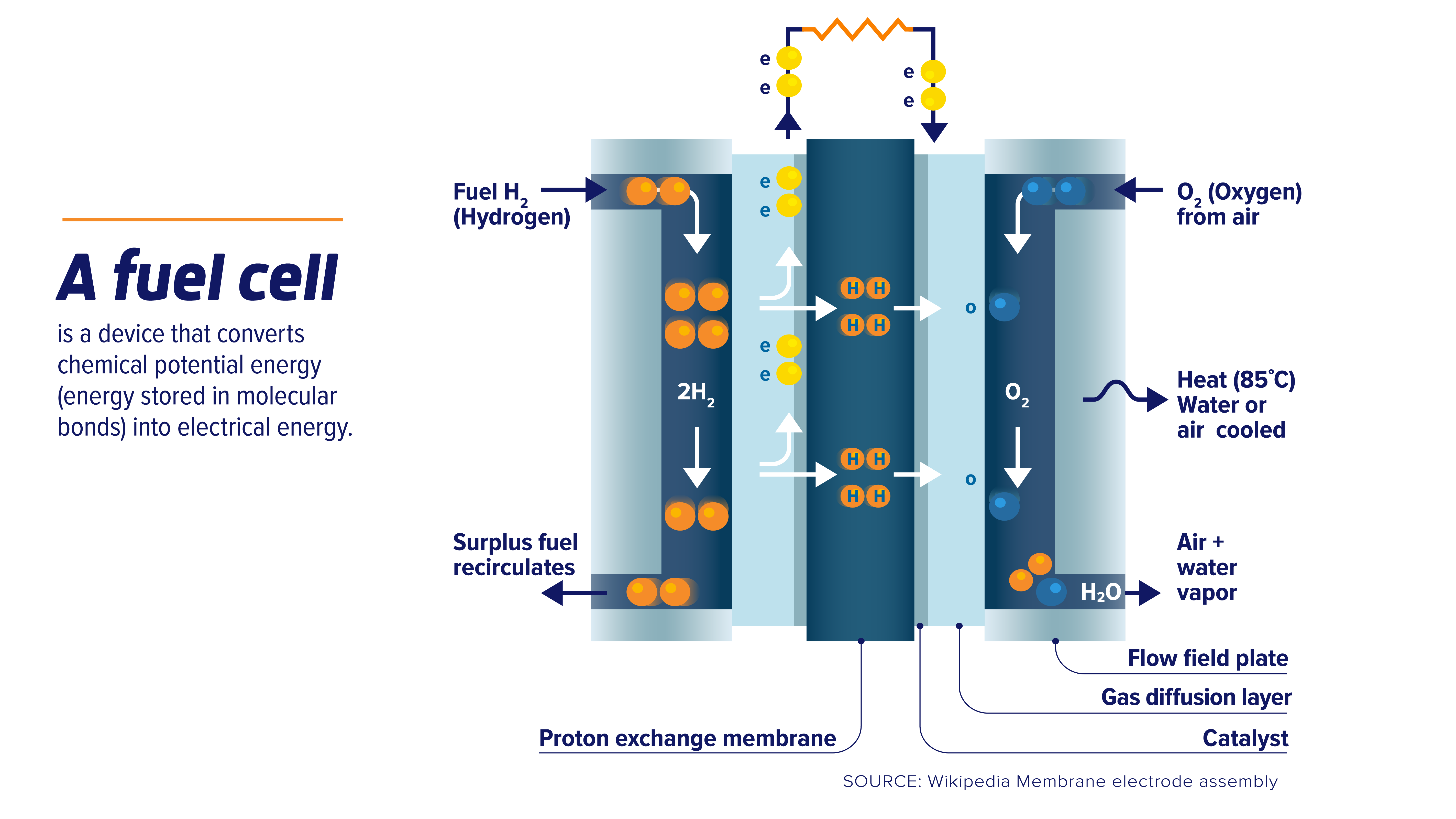
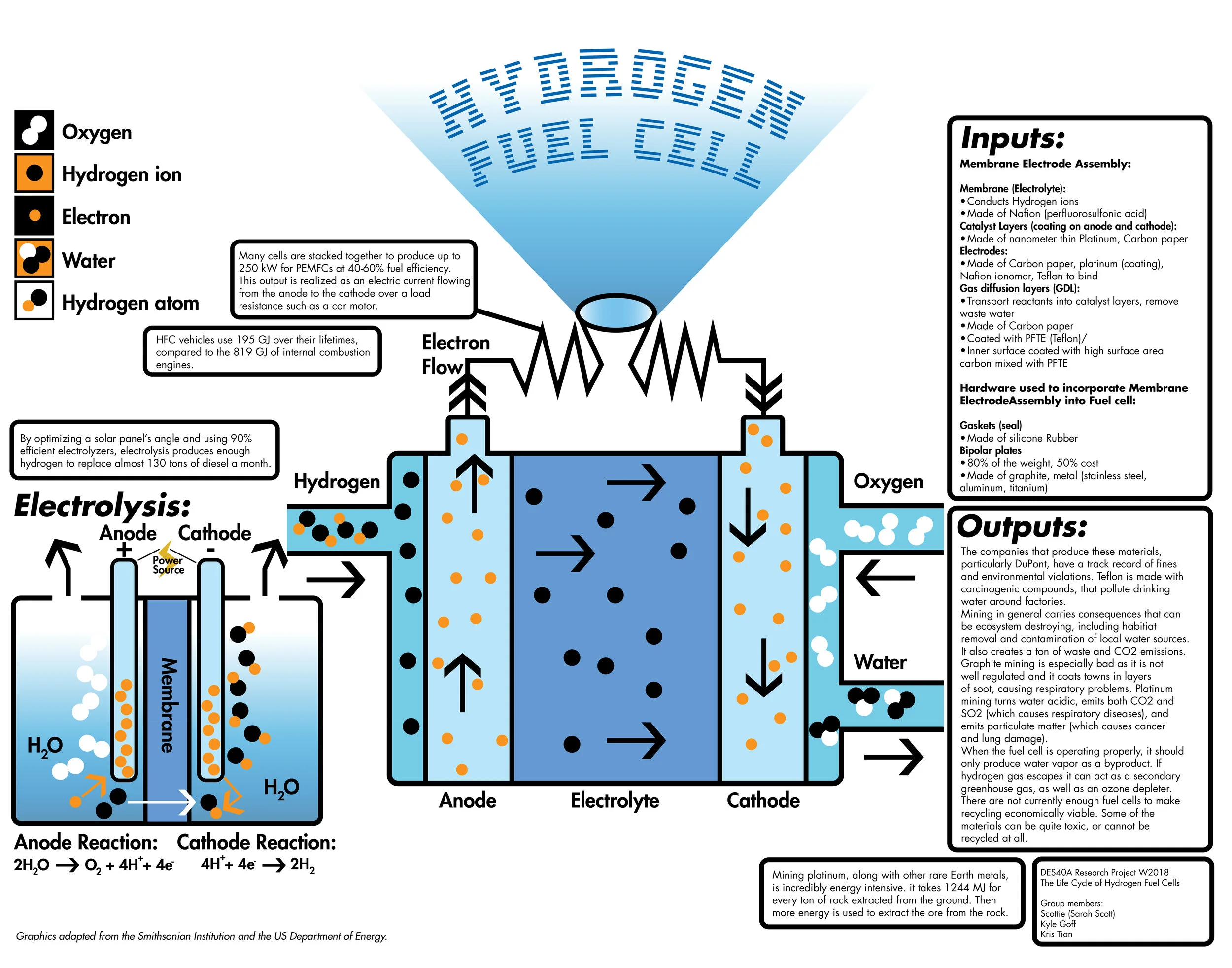
Hydrogen fuel cells are electrochemical devices that convert the chemical energy stored in hydrogen and oxygen into electrical energy, producing water as a byproduct. The process involves the following steps:
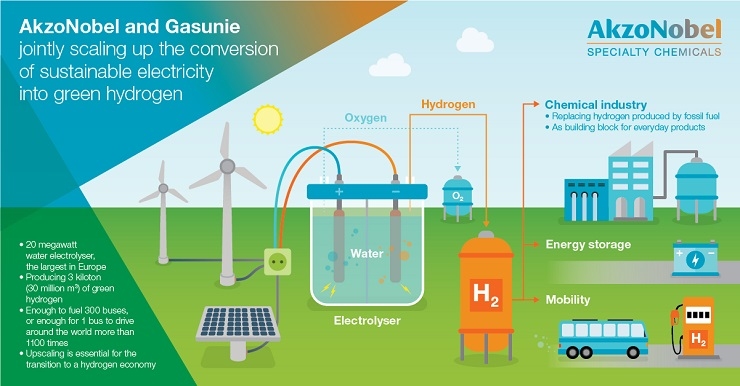
- Hydrogen and oxygen are supplied to the fuel cell. Hydrogen is typically stored in a compressed or liquid form, while oxygen is drawn from the ambient air.
- Hydrogen and oxygen are separated into ions and electrons. The hydrogen molecules are split into protons (H+) and electrons (e-) at the anode, while the oxygen molecules are reduced to oxygen ions (O2-) at the cathode.
- Ions pass through an electrolyte. The protons from the anode pass through a proton-conducting electrolyte, such as a polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM), while the oxygen ions from the cathode remain on that side.
- Electrons flow through an external circuit. The electrons from the anode travel through an external circuit, generating an electrical current.
- Protons and oxygen ions combine to form water. The protons from the electrolyte and the oxygen ions from the cathode combine to form water molecules (H2O).
Advantages of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Hydrogen fuel cells offer several compelling advantages over conventional combustion-based energy sources:
- Zero emissions: Hydrogen fuel cells produce only water as a byproduct, making them an environmentally friendly option with no greenhouse gas emissions.
- High efficiency: Fuel cells can convert up to 80% of the chemical energy in hydrogen into electrical energy, making them significantly more efficient than combustion engines.
- Quiet operation: Fuel cells operate quietly, reducing noise pollution compared to traditional internal combustion engines.
- Scalability: Fuel cells can be scaled up or down to meet various power requirements, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
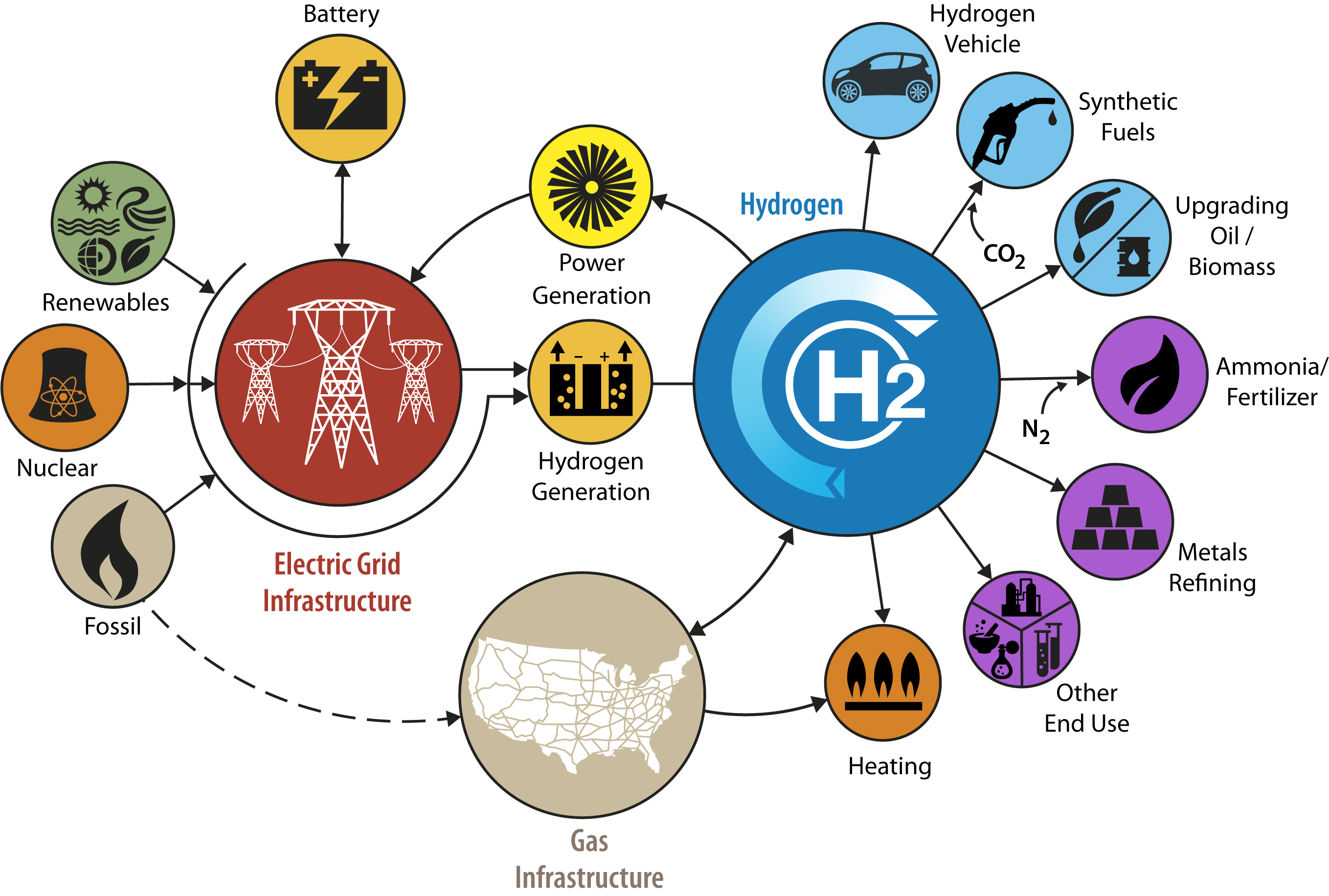
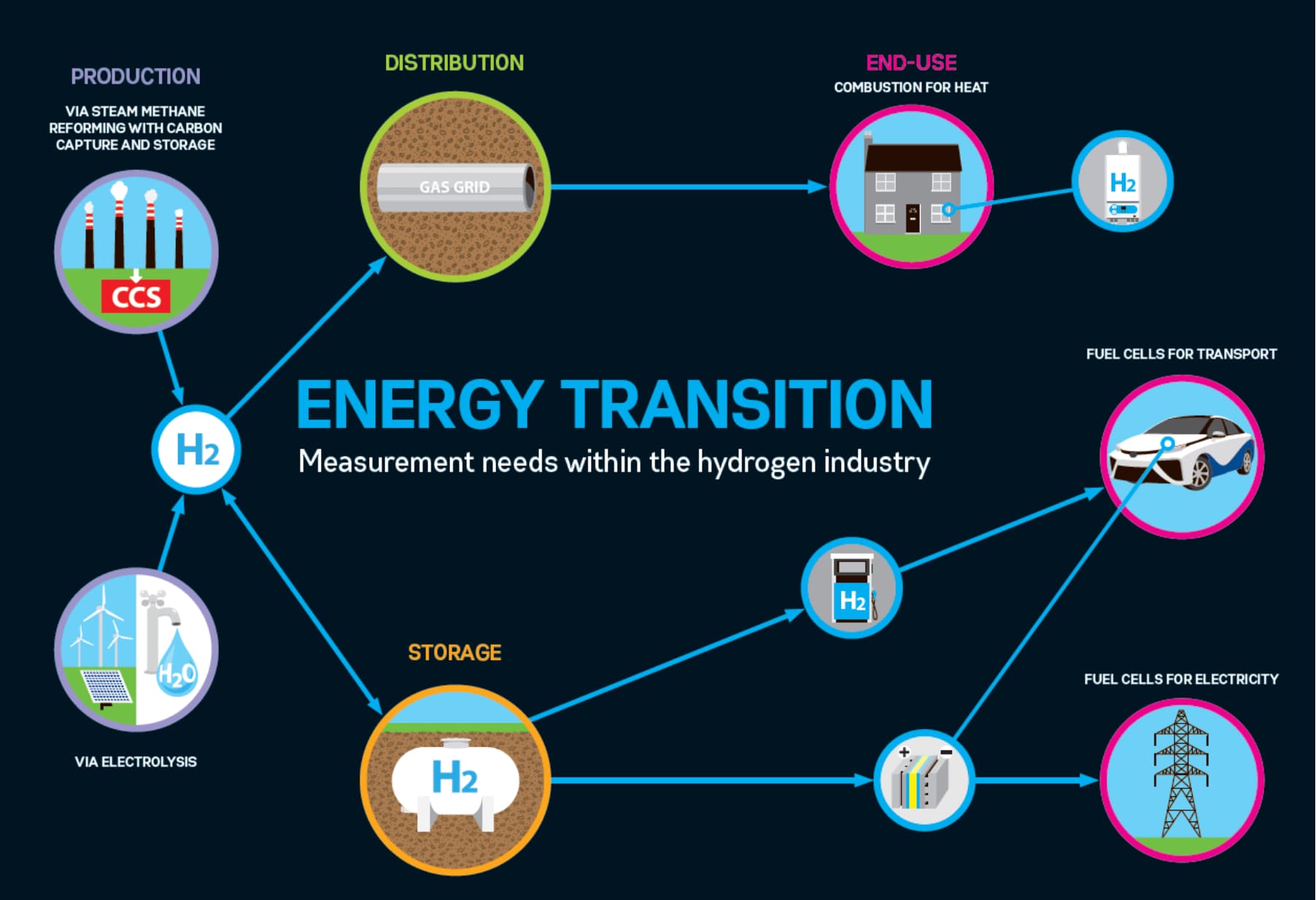
Applications of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
The versatility of hydrogen fuel cells enables them to find applications in various sectors:
- Transportation: Fuel cells are particularly well-suited for powering electric vehicles, offering extended range, rapid refueling, and zero emissions.
- Stationary power generation: Fuel cells can provide reliable and clean power for residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
- Portable power: Fuel cells can be used in portable devices, such as laptops and smartphones, providing extended battery life and eliminating the need for frequent charging.
- Grid balancing: Fuel cells can assist in balancing the electrical grid by providing backup power during peak demand or integrating intermittent renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite their numerous advantages, hydrogen fuel cells still face some challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption:
- Cost: The production and infrastructure costs associated with hydrogen fuel cells are currently high, hindering their commercial viability.
- Hydrogen storage and distribution: Developing safe and efficient methods for hydrogen storage and distribution is crucial for the scalability of fuel cell technology.
- Durability and lifespan: Improving the durability and lifespan of fuel cell components is essential for long-term operation and cost-effectiveness.
Nevertheless, significant efforts are underway to overcome these challenges. Governments, research institutions, and industry leaders are investing heavily in research and development to reduce costs, improve performance, and establish a comprehensive hydrogen infrastructure.
As the world transitions towards a cleaner and more sustainable energy future, hydrogen fuel cells are poised to play a pivotal role. Their zero-emission nature, high efficiency, and versatility make them an attractive alternative to fossil fuels. By addressing the current challenges and continuing to advance the technology, hydrogen fuel cells have the potential to revolutionize the way we generate and use energy.
Conclusion
Hydrogen fuel cells represent a promising technology that holds immense potential for a sustainable energy future. Their ability to convert hydrogen and oxygen into electrical energy with zero emissions and high efficiency makes them an environmentally friendly and efficient alternative to conventional energy sources. While challenges remain in terms of cost, hydrogen storage, and durability, ongoing research and development efforts are paving the way for the widespread adoption of fuel cell technology. As the world strives towards decarbonization and a cleaner energy landscape, hydrogen fuel cells are poised to become a key player in the transition to a more sustainable future.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Hydrogen Fuel Cells: A Clean and Efficient Energy Source for the Future. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!